MySQL WHERE Clause
The WHERE clause can be used within an SQL statement to narrow the result set down to a given set of criteria.
For example, you can narrow down the results of a SELECT statement like this:
The above statement selects all records from the actor table in the sakila database where the value of the first_name column is equal to nick (not case-sensitive).
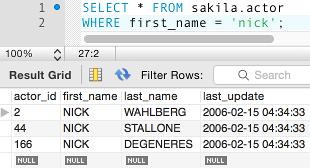
Without the WHERE clause, the statement would return all records in the table. Depending on the database, this could potentially be thousands or even millions of records. If we were only interested in finding actors with a first name of "Nick" we would have a big job ahead of us.
The WHERE clause is also used with the SQL UPDATE statement to specify the record that is to be updated:
Without the WHERE clause, all records would be updated.
The examples on this page use the Sakila sample database.