MySQL ORDER BY Clause
The ORDER BY clause can be used within an SQL statement to sort the result set by one or more fields.
Ascending Order
You can sort the results of a SELECT statement like this:
The above statement selects all records from the actor table in the sakila database, then orders them by the actor_id field in ascending order.
Result:
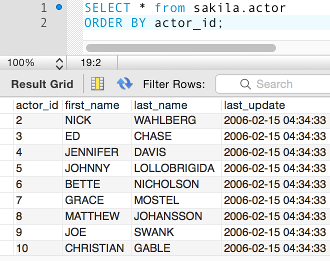
The ORDER BY clause orders the results in ascending order by default.
You can also add ASC to the clause in order to be explicit about this. Like this:
Descending Order
You can use DESC so that the results are listed in descending order. Like this:
Result:
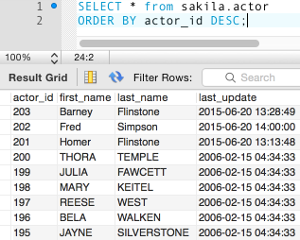
Ordering By Multiple Fields
You can use more than one field in your ORDER BY clause. The results will be ordered by the first column specified, then the second, third, and so on.
To demonstrate this, consider the following SQL statements:
The only difference between the above two SQL statements is that the second one has DESC on the last_name field. Therefore, the results will be ordered, first by the first_name column in ascending order, then by the last_name in descending order. This is in contrast to the first statement which orders both columns in ascending order.
Below is the result of those two statements.
First statement:
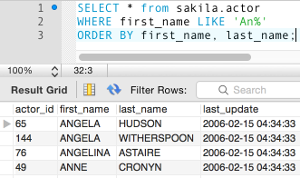
Second statement (descending last_name):
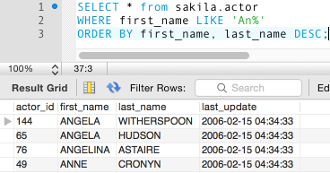
Note the order of the first two records in each example. Although the records were ordered by first_name, there are two first_name records with the same value (i.e. Angela). This is when last_name DESC comes into effect and it results in switching the placement of the first two records.
The examples on this page use the Sakila sample database.