Access 2016: Create a Relationship
Access allows you to create relationships between tables so that you can query related data from multiple tables.
In relational database terms, a relationship is a situation where multiple tables can contain related data that is linked by a common field.
A relationship consists of a parent table and a child table. The child table references the parent table by having a field that matches a field in the parent table. The child's field is referred to as a foreign key. The parent's field is the primary key.
In a relationship, any data entered into the child's foreign key field must match a value from the parent's primary key field.
By ensuring that the foreign key's data matches data in the primary key, we know that all records in the child table will have an associated record in the parent table.
So we can create a one-to-many relationship between the Albums and Artists table. Our relationship will determine that an artist can have many albums, but an album can only belong to one artist.
-

Open the Relationship Dialog
Click Relationships from the Database Tools tab on the Ribbon.
The Show Tables dialog box should appear. If it doesn't appear, click Show Tables.
If you have not yet created any relationships, the Show Table dialog box automatically appears when you click the Relationships button.
If you have previously created a relationship, the current relationships will appear instead.
-

Select the Tables
Select both the Artists and Albums tables from the list and click Add.
Click Close to close the dialog box.
-

Create the Relationship
Click and drag the Albums.ArtistId field over the Artists.ArtistId field and release.
The Edit Relationships dialog box appears.
-

Edit the Relationship
Check Enforce Referential Integrity and click Create.
The Enforce Referential Integrity option will ensure that child records cannot reference a non-existent parent.
So if a user tries to enter an album with an ArtistId that isn't in the Artists table, Access will prevent them from doing so.
Access will also prevent the user from deleting an artist that has albums attached.
However, you can change how Access deals with deletes and data updates with the Cascade Update Related Fields and Cascade Delete Related Fields. Selecting these options will delete (or update) all related records whenever a primary record is deleted/updated.
-
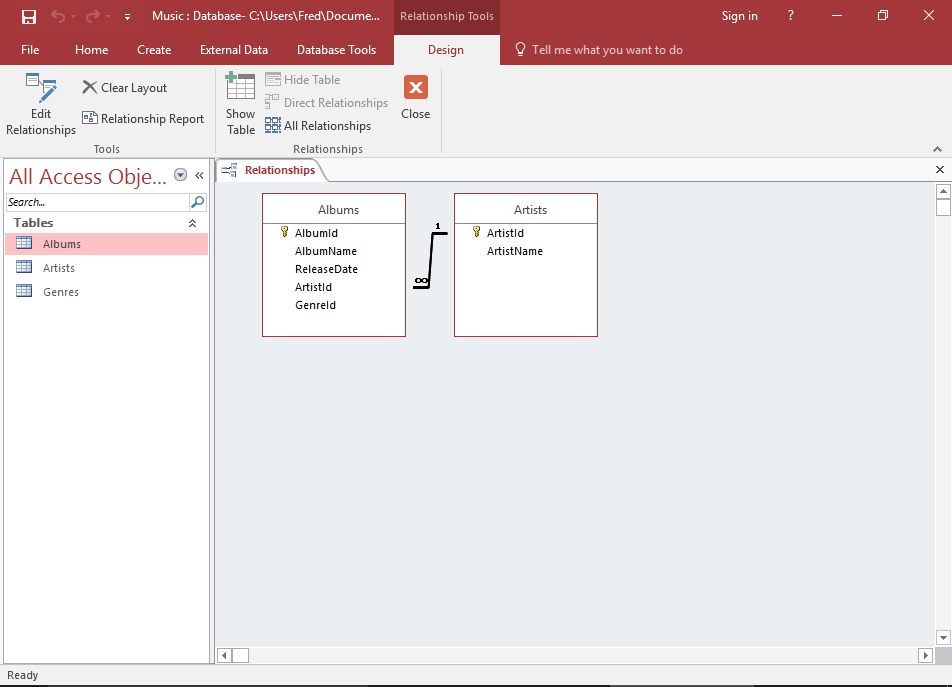
The Relationship
A diagram now appears, representing the relationship.
Save the relationship by pressing Ctrl+ S, right-clicking on the tab and clicking Save, or clicking the X icon to close the relationship.
So now that we've established the relationship, we can query data across both tables and get meaningful results. For example, we can now look up how many albums an artist has released. Or we could find out which artist released a given album. And more.
Types of Relationships
There are three types of relationships:
- One-to-One
- A row in table A can have only one matching row in table B, and vice versa.
- One-to-Many (or Many-to-One)
- A row in table A can have many matching rows in table B, but a row in table B can have only one matching row in table A.
- Many-to-Many
- A row in table A can have many matching rows in table B, and vice versa. This is achieved through the use of a third table (commonly called a junction table) that contains lookup data for both tables.